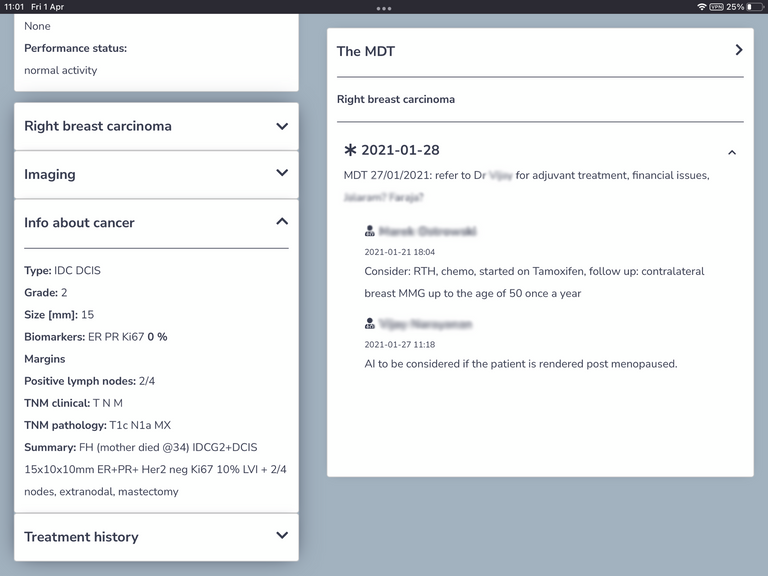
TheMDT.online is a web-based platform which securely gathers relevant patient data into a single patient dashboard where medical professionals can review and discuss a patient’s case at both physical and virtual meetings, facilitating multidisciplinary care for breast cancer patients.
What is a Multidisciplinary team approach in breast cancer care?
Cancer care and treatment is complicated, requiring a team-based model of care for cancer patients. Multidisciplinary Teams (MDTs), also known as tumor boards, play a vital role in contemporary cancer care and are often considered the “gold standard” for clinical decision making in diagnosis and treatment. In MDT meetings, a group of specialists consisting of medical, nursing and allied professionals regularly discuss their patients to cooperatively decide on the most beneficial course of treatment tailored to their patients’ needs.
Evidence from clinical studies consistently indicates that successful implementation of MDTs by hospitals leads to improved outcomes in terms of diagnosis, treatment planning, patient survival, patient satisfaction, and clinician satisfaction as a result of successful cooperation and communication. MDTs have been widely implemented throughout Europe, North America and Australia; in the UK NHS, they have become a mandatory element of cancer care.
The Gold Standard for Collaborative Approach to Cancer Care
However, MDTs are not standard practice worldwide; high costs both in terms of clinicians’ time and money, as well as the lack of experienced specialists in deprived areas have severely limited the implementation of multidisciplinary approaches in parts of Africa, Asia and South America.
Where MDTs are implemented, the preparation and gathering of information for holding MDT meetings is time-consuming and cumbersome. Data presented at MDT meetings comes from various disparate sources such as medical records, lab information systems, and is usually gathered independently, expending valuable time in preparation.

How does MDT.Online help?
TheMDT.online addresses these issues through a web-based platform which securely gathers relevant patient data into a single patient dashboard where medical professionals can review and discuss a patient’s case at both physical and virtual meetings.
It is a platform which facilitates multidisciplinary care.
Using our secure online MDT:
Clinicians can enter information about their patients to help inform a rigorous diagnosis with other medical participants.
An MDT consisting of the diagnosing physician and selected specialists is then formed, with each able to add their comments in real-time, either in combination with a teleconferencing system, or asynchronously dropping in and out of the continuing discussion surrounding the given patient.